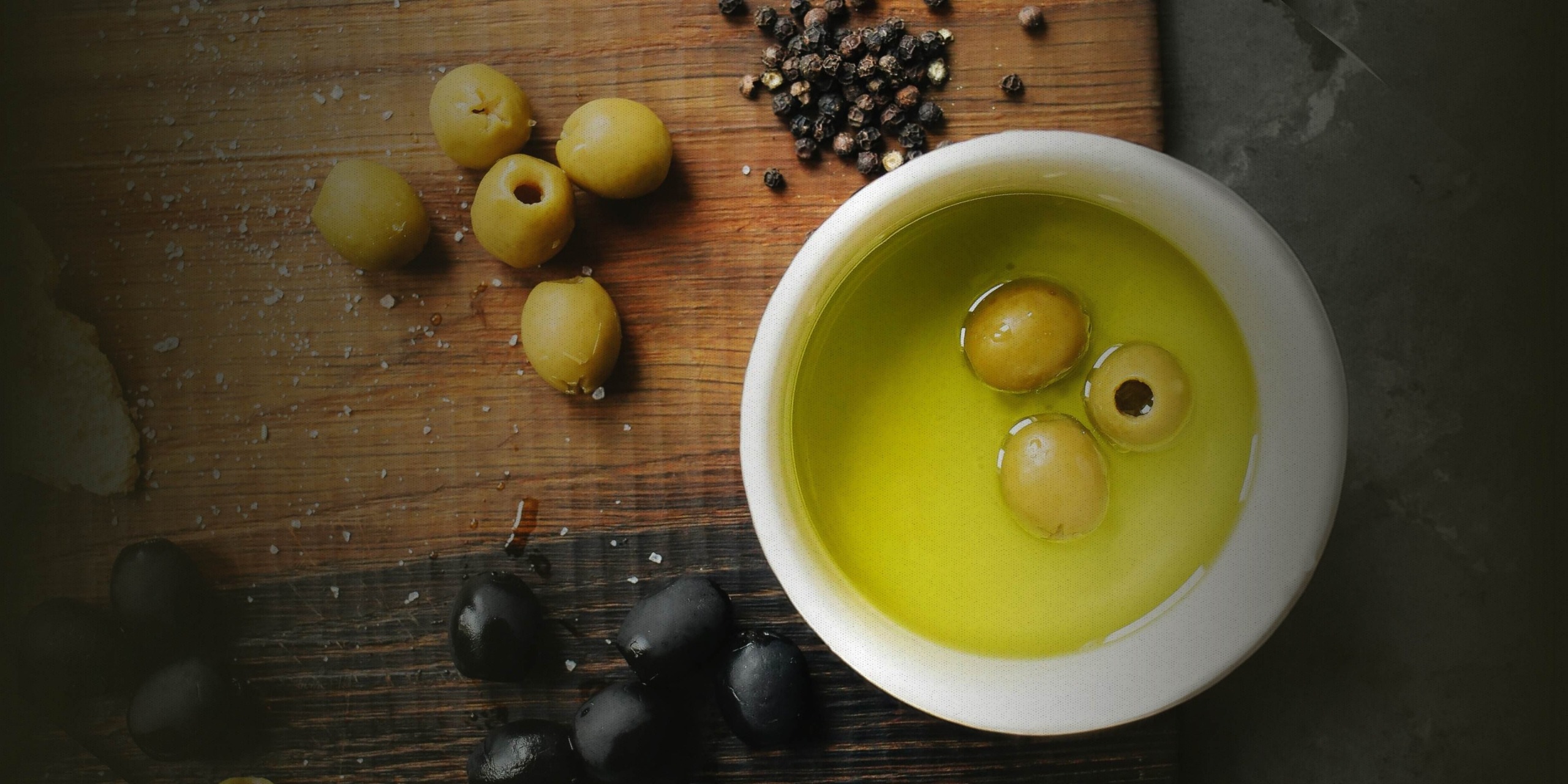
The impact of Ancient Greece on the modern world is immeasurable. From government and philosophy to art, math, science, and medicine, the roots of many of our advancements trace back to the Greeks. We can also thank them for what they famously refer to as “liquid gold”, also known as olive oil, a gift that continues to benefit our diets and health today.
While we’ve discussed the benefits of olive oil before, the increasing production and use of seed oils such as canola, corn, and soy prompt us to revisit this topic. It’s crucial to understand that not all oils, including olive oils, are created equal.
Olive oils vs. Seed oils
Whether you’re coating a pan, adding to a baking mixture or drizzling over a meal, both types of oils have been long been staples in the kitchen. However, that’s where most of the similarities between the two end.
You see, olive oil tends to have a richer flavor and aroma, compared to the milder, almost neutral profile of seed oils.
But the most significant difference lies in their impact on your health. While both oils are healthier than butter, seed oils are high in things like polyunsaturated fats (aka omega-6), especially linoleic acid. Although our bodies require small doses of linoleic acid, research shows that excessive intake can lead to chronic inflammation, cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer’s, obesity, diabetes, and various neurological and psychiatric issues. In today’s Western diet, many people consume up to 20 times more omega-6 fats than omega-3 fats, exacerbating these risks.
On the other hand, olive oil is packed with monounsaturated fats, which are known to promote heart health by improving cholesterol levels.
Choosing quality olive oils
Selecting high-quality olive oil is crucial for maximizing its health benefits and enjoying its rich flavors. Some things to consider include:
- Extra Virgin: Always opt for “extra virgin” olive oil. This designation means the oil is made from the first cold pressing of olives without any heat or chemicals, preserving its natural flavors and nutrients. Extra virgin olive oil is considered the highest quality, retaining the most antioxidants and flavor compounds.
- Cold-Pressed: Cold pressing refers to the method of extracting olive oil without applying heat, which helps maintain the oil’s natural properties and ensures a more vibrant flavor profile. This method is crucial for preserving the beneficial compounds found in olives.
- Dark Bottles: Olive oil should be stored in dark glass bottles or cans to protect it from light, which can accelerate degradation. Exposure to light and heat can diminish the oil’s quality and shorten its shelf life.
- Harvest Date: Look for a harvest date on the label, which indicates when the olives were picked. Olive oil is best consumed within a year of this date. Fresher oils have a more intense flavor and higher antioxidant levels.
- Certification: Check for certifications from reputable organizations, such as the California Olive Oil Council (COOC) or the International Olive Council (IOC). These certifications help ensure that the oil is authentic and meets high standards of quality.
Going Greek
Ancient Greece was one of the first pioneers in olive oil, and to this day, it still produces some of the best-quality olive oil in the world. Why?
- Climate and Soil: Greece’s Mediterranean climate and varied soil types create optimal conditions for olive cultivation. The combination of warm temperatures, abundant sunshine, and well-drained soil enhances the flavor and nutritional profile of Greek olive oil.
- Traditional Practices: Many Greek olive oil producers use traditional, organic farming methods that avoid synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. This commitment to organic practices helps preserve the oil’s authentic taste and nutritional benefits.
- Harvesting Techniques: Greek producers often harvest olives by hand and use techniques that minimize damage to the fruit. This careful handling helps maintain the oils quality and flavor.
- Regulations and Standards: Greece has stringent regulations to ensure the quality and authenticity of its olive oil. Many Greek olive oils are certified and undergo rigorous testing to confirm their purity and adherence to high standards.
Needless to say, Greece still takes its passion for olive oil seriously, and it’s definitely something to consider when you’re looking to make an impact on your diet and health.